| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Summary | Scaling the cluster. |
| Categories | openstack |
| Difficulty | 2 |
| Author | Tytus Kurek tytus.kurek@canonical.com |
Overview
Duration: 3 minutes
Before you get started!
Welcome to OpenStack!
In this series of tutorials, we will walk you through all the necessary steps to install, configure and get started with OpenStack. Using just three dedicated machines, you will learn how to deploy OpenStack in highly available, multi-node, production-grade clusters.
This tutorial is the fourth in the “Phase 2 - Deploy OpenStack” series.
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is a collection of open source projects designed to work together to form the basis of a cloud. OpenStack can be used for both private and public cloud implementation.
What is Sunbeam?
Sunbeam is an upstream project under the governance of the OpenInfra Foundation (OIF), which was created to lower the barrier to entry for OpenStack, simplify its adoption process, and set the foundation for an autonomous private cloud. Sunbeam uses cloud-native architecture and total bottom-up automation to make OpenStack more accessible to newcomers and to help users get to grips with the platform immediately.
What is MicroStack?
MicroStack (based on Sunbeam) is an OpenStack distribution designed for small-scale cloud environments. While it is available with full commercial support from Canonical, it can also be self-deployed with no friction, effectively eliminating the need for a paid consulting engagement. MicroStack currently includes core OpenStack services only, but is expected to evolve quickly to ensure full feature parity with Canonical’s Charmed OpenStack soon.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
- Add additional nodes to the cluster
- Enable high availability in a multi-node deployment
You will only need:
- Theoretical knowledge of OpenStack gained by completing all tutorials in the “Phase I - Learning OpenStack” series
- Three fresh physical machines with:
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS installed,
- A minimum of 32 GB of free memory
- 200 GB of SSD storage available on the root disk
- At least one un-partitioned disk of at least 200 GB in size
- Two network interfaces:
- A primary network interface for access to the OpenStack control plane
- A secondary network interface for remote access to cloud VMs
- OpenStack cloud bootstrapped and configured
Reference configuration
Duration: 5 minutes
This section provides reference configuration used for the purpose of this tutorial.
! Reference configuration
Note that in your environment those values might be different and might need to be adjusted accordingly.
Machine
For the purpose of this tutorial, the following machines are used:
| Machine | FQDN | Un-partitioned disk | Roles |
|---|---|---|---|
| sunbeam01 | sunbeam01.example.com | /dev/sdb | control, compute, storage |
| sunbeam02 | sunbeam02.example.com | /dev/sdb | control, compute, storage |
| sunbeam03 | sunbeam03.example.com | /dev/sdb | control, compute, storage |
Control plane networking
The network associated with the primary network interface requires a range of approximately 10 IP addresses that will be used for API service endpoints.
For the purposes of this tutorial, the following configuration is in place:
| Network component | Value |
|---|---|
| CIDR | 172.16.1.0/24 |
| Gateway | 172.16.1.1 |
| Address range | 172.16.1.201-172.16.1.220 |
| Interface name on machine | eno1 |
External networking
The network associated with the secondary network interface requires a range of IP addresses that will be sufficient for allocating floating IP addresses to VMs. This will, in turn, allow them to be contacted by remote hosts.
For the purposes of this tutorial, the following configuration is in place:
| Network component | Value |
|---|---|
| CIDR | 172.16.2.0/24 |
| Gateway | 172.16.2.1 |
| Address range | 172.16.2.2-172.16.2.254 |
| Interface name on machine | eno2 |
Add additional nodes to the cluster
Duration: 10 minutes
In this tutorial we’ll add two additional nodes to the cluster.
Create registration tokens for other nodes
Registration tokens have to be created first for other machines to be able to join the cluster.
In order to create a registration token for the second machine (sunbeam02.example.com), execute the following command on sunbeam01 machine:
$ sunbeam cluster add --name sunbeam02.example.com
Sample output (token):
Token for the Node sunbeam02.example.com: eyJuYW1lIjoic3VuYmVhbTAyLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwic2VjcmV0IjoiYTNiMDM3NTBlMGNiNzc0N2FmNjcxYTMwZjJlMzYyY2E3Njk3YTM0MDQ3NjI5MjdmMTdhN2MxNmVlOTI5MGNlMSIsImZpbmdlcnByaW50IjoiODM2NDI4YzIzNzA4Y2RhYmNhNTJiYzU0Njg4ZTMxYjQ2ZDllMWIxYTcyODYyMGE3NzZkYzg5NWVkZmI3NDYxOCIsImpvaW5fYWRkcmVzc2VzIjpbIjE3Mi4xNi4xLjEwMTo3MDAwIl19
In order to create a registration token for the third machine (sunbeam03.example.com), execute the following command on sunbeam01 machine:
$ sunbeam cluster add --name sunbeam03.example.com
Sample output (token):
Token for the Node sunbeam03.example.com: eyJuYW1lIjoic3VuYmVhbTAzLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwic2VjcmV0IjoiN2NiNDM4N2Q4ZGFiZmQ3MTRlNjgxNzAxZjE4MDIyMDEyYzE5NjVmZGY1MjE2NDViNmI2NzZjZTU1ZDhiZTQwNyIsImZpbmdlcnByaW50IjoiODM2NDI4YzIzNzA4Y2RhYmNhNTJiYzU0Njg4ZTMxYjQ2ZDllMWIxYTcyODYyMGE3NzZkYzg5NWVkZmI3NDYxOCIsImpvaW5fYWRkcmVzc2VzIjpbIjE3Mi4xNi4xLjEwMTo3MDAwIl19
Install OpenStack snap on other nodes
In order to install OpenStack snap on other nodes, execute the following command on sunbeam02 and sunbeam03 machines:
$ sudo snap install openstack --channel 2024.1/beta
Prepare other nodes
In order to prepare other nodes for OpenStack usage, execute the following command on sunbeam02 and sunbeam03 machines:
$ sunbeam prepare-node-script | bash -x && newgrp snap_daemon
Add other nodes to the cluster
In order to add other nodes to the cluster with control, compute and storage roles, execute the following command on sunbeam02 and sunbeam03 machines:
$ sunbeam cluster join --role control --role compute --role storage --token <token>
Note that the value of the token must match the value obtained in the “Create registration tokens for other nodes” section.
! sunbeam cluster join
This command takes a while to finish. Please, be patient.
When prompted, enter the following values:
- Disks to attach to MicroCeph - type the value of the
Un-partitioned diskfield next to thesunbeam01machine from the “Machines” sub-section of the “Reference configuration” section and pressEnter. - Free network interface that will be configured for external traffic - type the value of the
Interface name on machinefield from the “External networking” sub-section of the “Reference configuration” section and pressEnter.
Sample output:
Disks to attach to MicroCeph (comma separated list) (): /dev/sda
Free network interface that will be configured for external traffic [eno2] (eno2): eno2
Once finished, you should be able to see the following message:
Node joined cluster with roles: control, compute, storage
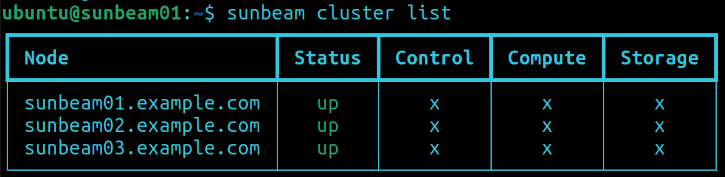
You should now be able to see all three machines on the list of cluster nodes:
$ sunbeam cluster list
Sample output:
Resize the control plane
In order to resize the control plane for high availability, execute the following command on sunbeam01 machine:
$ sunbeam cluster resize
! sunbeam cluster resize
This command takes a while to finish. Please, be patient.
Once finished, you should be able to see the following message:
Resize complete.
Next steps
Duration: 2 minutes
Congratulations! You have reached the end of this tutorial.
You can now move to the next tutorial - “5. MAAS” - or explore other tutorials.
In this tutorial, you have learnt how to:
- Add additional nodes to the cluster
- Enable high availability in a multi-node deployment